Some time in my career, I was working in a RFID tracking system and I was designing the real time event notification web application for that, I was using Google Map API to show the activities on a particular facility/ floor map, where RFID sensors were mounted. I tried lot of techniques and APIs and finally, I could able to push messages to the clients.. Now the question is “how did I do that???” It was a long back and at that time there were very few APIs available, which were providing server side pushing. I took the DWR Reverse AJAX and in a layman’s way to explain, clients were subscribing for the messages for a particular criteria with the server. But to be very honest, let’s say after some 7 - 8 hours, the browsers used to be almost inactive and user couldn't even do anything, may be because of memory. Few years back, when I started using the TweetDesk a Chrome app, I realized it uses the same technique to get the messages and it is damn good and efficient. I was always very eager to know what exactly and how they are doing that.. Today facebook.com, amazon.com are very popular and they also follow some kind of the same approach… One more thing, I noticed with firebug, that for most of the operations, there is a AJAX call and only the data is flowing in terms of JSON/ text; there is no form submit to any action.. And the biggest advantage is that they are user-friendly, interactive and kick ass fast.
Long time back, there was a standard approach for all the web applications. Most of the cases, everyone was following the MVC or MVC 2 design with a service layer and DAO layer. And those days one application means a huge and fat war or an ear. Companies were using heavy application containers like weblogic and jboss, with lot of dependency. It was like a fat ugly man needs an extremely customized environment to live his life, or else he will die in no time. After that some time back companies were moving towards the SOA. A big application was further divided in to small chunks and they were interacting with each other by messages.. SOAP based web services were very powerful technique to interact with services, but now the world is going towards RESTful web services as it is simple and easy to develop. With the SOA the applications were really simple and maintaining a low cohesion. The applications used to be light weight and the servers used to be healthy all the time. But still there was a room for improvement, why the UI elements are getting streamed from server and consuming a major band width of the network.. In order to answer this question, designers moved the MVC to front-end and back end is now only the services.. If you are a back-end developer, you will be thinking, how it is possible and may be feeling insecurity about your job.. But believe me, now it is time to adapt the so called ugly JavaScript to develop beautiful and interactive applications. As the MVC concerned with front-end, there are lot of JavaScript APIs are available. So I can now conclude something that all the modern web sites like facebook.com, amazon.com and some Chrome apps like TweetDesk are using the same concept.
I was part of the Spring One Conference India Dec, 2012 and there the things were got cleared with a talk from Jeremy Grelle. Jeremy is a Spring Source Staff Engineer and one of the open source contributor for many projects.. Next, I am going give a picture of what Jeremy presented in that conference. In this article, I will take you to “Where we’ve been”, “Where we’re going” and “How we will get there”.
Static Web Pages with HTML:
When the www started, all the pages were static and served from server. There used to be separate page for separate data. The world was with URL and links.
- Pros:
- Low Computation: As they are static, there is hardly any computations from a programmer point of view.
- Highly Cacheable: They are very easy and perfect candidate for caching.
- Highly Indexable: They are easily get indexed by leading search engines for their static data content.
- Cons:
- Hard to Update: If you need to change anything, you have to go to the HTML file and change that and a developer is required for the same.. Bad dependency; Isn’t it?
- No Personalization: You can’t have something which you really looking for.. You have to see a generic view, even if you are not bothered about the rest 90% of the content.
- Poor UI: UI used to be poor with bad response from server.
After some time, when the requirements and needs changed, pages were dynamic on user inputs. Users could able to get dynamic data on the same page.
- Pros:
- Dynamic: Now the pages went dynamic depending on the user inputs and different other criteria’s.
- Selectively Cacheable : As the pages were dynamic, so dynamic contents were not applicable for caching.
- Highly Indexable: They were also well indexed by the search engines.
- Personalization: As the user is able to provide inputs, they could able get the user a view that user is looking for.
- Cons:
- High Computation: To make a page dynamic, it required a computation overhead in different manner. Lot of scripting technologies had been adopted to create dynamic web pages.
- Hard to Create: Same page different data representations made very difficult for the browser to cache.
- Poor UI: Even though the pages went dynamic, the UI used to be poor, less interactive and less responsive.
Introduction to JavaScript to the web development made the pages bit more interactive and responsive. Developers started using JavaScript for basic form validation and other activities in DOM.
- Pros:
- Enhanced Usability: With the help of JavaScript, developers could able to give a good response to some of the actions, where there is no back-end data involvement.
- Reduced Trips to Server: As most of the validations went front-end, there was a network band width save. Developers eliminated the validation calls from server-side.
- Cons:
- Abused Annoyed Users: As JavaScript is a client-side technology, lot of users started misusing that.
- Business Logic Often Implemented Twice: With reference to validation, sometimes the validation logic and other business logic were implemented both at client side and server-side.
Google came up with a new approach of interacting with server. With the help of Web 2.0, Google launched Map API and Gmail. Server interaction made possible both synchronously and asynchronously with out submitting an action to the server.
- Pros:
- Killer UI: With the introduction of AJAX, the look and feel of the UI went out of the world with lot of UI components.
- More Responsive Apps: User were able to interact with application easily without much effort and as with AJAX only the data used to be get streamed the via network, the response for a particular action used to be very fast.
- Cons:
- Difficult to Cache: As there are hardly any static content, at least, it was very difficult to cache the whole page.
- Impossible to Index: With dynamic data, indexing a page for a search engine was quite impossible.
- Required JavaScript: With introduction to AJAX, there was a need for skilled UI developers in industry.
After some time, JavaScript proved to be a clumsy language unsuitable for serious application development. This has been largely due to inconsistent implementations of the language itself and the Document Object Model in various browsers, and the wide spread use of buggy copy-and-paste code. Run time errors were so common (and so difficult to debug), that few programmers even tried to fix them, as long as the script behaved more or less the way it was supposed to, scripts often failed completely in some browsers. At that moment the industry was again fallen back to the basic HTML way of presenting the view. And this is the time when some MVC 2 frameworks were evolved. Unobtrusive JavaScript is a general approach to the use of JavaScript in web pages. Though the term is not formally defined, its basic principles are generally understood to include Separation of functionality (the "behavior layer") from a Web page's structure/content and presentation, best practices to avoid the problems of traditional JavaScript programming (such as browser inconsistencies and lack of scalability) and progressive enhancement to support user agents that may not support advanced JavaScript functionality.
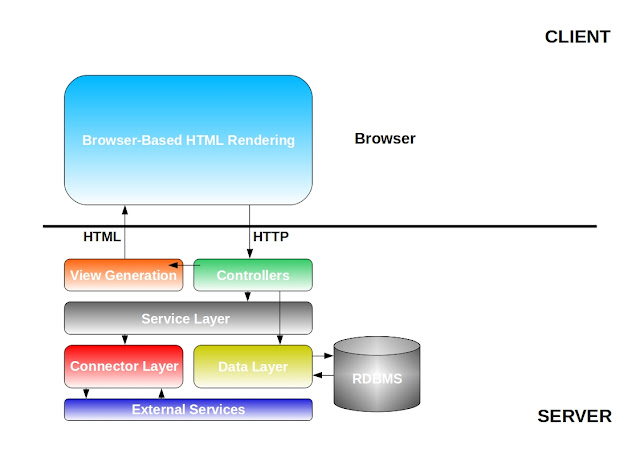 |
| Architecture of a Old Web Application |
- Pros:
- Wider Compatibility: As again the UI started coming from server as a HTML, it has a better compatibility with wider range of browsers.
- Just as Rich UI: As the UI was getting streamed from server, it was a raw HTML with rich components.
- Just as Responsive: As designers were still stick to JavaScript for some non-business related activities, the response of some activities were still good.
- Cons:
- Higher development cost: Generally to make a simple application, now you need a big team with developers, architects and some managers to make sure everything happening as per the plan, which is a time consuming process..
- Requires thoughtful engineering: As you can’t make changes to the final product as it would have lot of dependencies and you never know one change will break how many other things. So you have to have a very good design looking at the future scope.
Over the time designers noticed one common thing in all approaches, i.e. there are unnecessary data like HTML are also flowing from server to client and that is a major problem for slowness of the application. Now there is a significant contribution to the JavaScript APIs from the open source contributors around the world. Business logic is no more part of the server, all moved to the front-end along with the MVC. Application state was started storing in front-end, only the permanent state has been stored in back-end. As there are no more MVC and business logic in backend, the back-end part of the applications are turning to services. SOA also has a greater impact on the current design, instead of thick fat web application, it is getting divided in to smaller chunks to make the back-end healthy and independent with each other. Introduction of RESTful web services made front-end directly interact with services. Recently Google announced the Chrome Laptops, which are totally on the browser, so looking at the current processor architecture and memory capacity of personal computers and laptops, the browser is capable of doing complex computations and also capable of storing significant data required for a particular page.
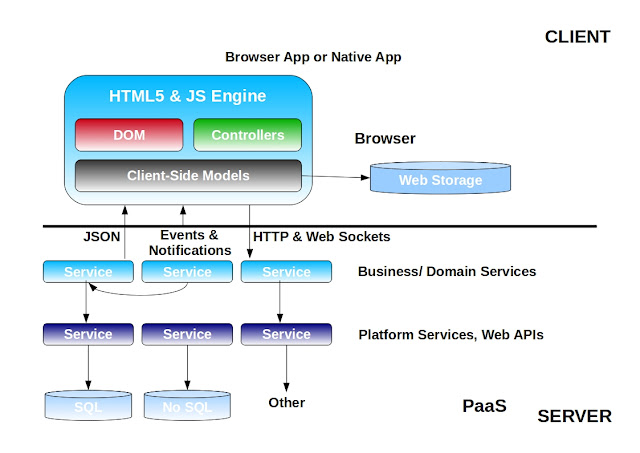 |
| Architecture of a Modern Web Application |
- Pros:
- Reduce server workload : As the MVC and business logic is moving to the client side, there is minimal computation at the server side, may be the CRUD operation on a object. And again with service call only the data is flowing in network, so there is a significant save in network band width.
- Application is highly cacheable: As the business logic and MVC is moving to front-end, front-end is making use of system resources to store data.
- Extremely rich UI: As I explained above, there are lot of contribution to some of the open source projects and there are lot of light weight JavaScript APIs are available now.
- Cons:
- Content not indexable: As the content is 100% dynamic, there is no scope for the search engines to index the page.
- JavaScript: Now it is the time to learn JavaScript and start using that. Lot of companies are recruiting dedicated UI developers.
- Often requires a modern browser: Along with JavaScript, there are some other technologies like HTML5 and CSS3 are also adopted with context to the new architecture.. So some time user need a updated browser to use the application.
With the current configuration standard of a personal computer or a laptop, this approach is proving it’s capability.. As discussed about some of the web sites like facebook.com, amazon.com, ebay.com etc. and some of the browser apps like TweetDesk, RSS Readers etc. are very popular for their performance.
The definition of back-end and front end are shifting to front-end != client and back-end != server. There are lot technologies are evolving and there is a huge support from the open source contributors. Now it is the time for a java developers to take interest in JavaScript and start learning the new technologies like css3, HTML5 with some JavaScript libraries like jQuery, s2js, cujo.js, scripted, SockJS, monty-hall, monty-hall-ui etc.
Even though, I have drafted this article for you guys, I want to give the credit to Jeremy Grelle, SpringSource Staff Engineer and open source contributor. I would also like to thank VMWare for inviting me to SpringOne India 2012 Conference.
I will soon be developing some small applications using this architecture and will probably deploy those in the Cloud, so that you people can play around that.